Factoring Polynomials
Multiplication of polynomials relies on the distributive
property. The reverse process, where a polynomial is written as a
product of other polynomials, is called factoring. For example,
one way to factor the number 18 is to write it as the product 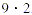 both 9 and 2 are factors of 18. Usually, only
integers are used as factors of integers. The number 18 can also
be written with three integer factors as both 9 and 2 are factors of 18. Usually, only
integers are used as factors of integers. The number 18 can also
be written with three integer factors as 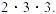
The Greatest Common Factor
To factor the algebraic expression 15m + 45, first note that
both 15 m and 45 are divisible by 15; 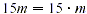 and and 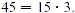 By the distributive property, By the distributive property,
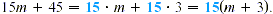
Both 15 and m+3 are factors of 15m + 45. Since 15 divides into
both terms of 15m + 45 (and is the largest number that will do
so), 15 is the greatest common factor for the polynomial 15m +
45. The process of writing 15m + 45 as15(m+3) is often called
factoring out the greatest common factor.
EXAMPLE
Factoring
Factor out the greatest common factor.
(a) 12p - 18q
Solution
Both 12 p and 18 q are divisible by 6. Therefore,
12p - 18q = 6·2p - 6·3q = 6 (2p -3q)
(b) 8x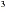 - 9x - 9x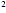 + 15x + 15x
Solution
Each of these terms is divisible by x .
8x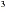 - 9x - 9x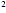 + 15x = (8x + 15x = (8x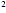 )x-
(9x)x + (15)x )x-
(9x)x + (15)x
= x(8x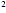 - 9x + 15) or (8x - 9x + 15) or (8x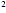 -
9x + 15)x -
9x + 15)x
One can always check factorization by finding the product of
the factors and comparing it to the original expression.
CAUTION
When factoring out the greatest common factor in an expression
like 2x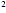 + x be careful to remember the 1 in the second term. + x be careful to remember the 1 in the second term.
2x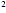 + x = 2x + x = 2x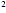 + 1x = x(2x + 1) not x(2x)
+ 1x = x(2x + 1) not x(2x)
|