Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a rule that can be written in the form,
|
y =
or f(x) = |
Ax2 + Bx + C Ax2 + Bx + C |
where A, B, and C are real numbers and A
≠ 0.
For example, the following are quadratic functions:
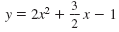 |
Here A = 2, B
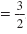 , and CThe following are functions but they are not quadratic functions:. , and CThe following are functions but they are not quadratic functions:.
|
| y = 4x2 + 5 |
Here A = 4, B = 0, and C = 5. |
| f(x) = -x2 + 2x - 8 |
Here A = -1, B = 2, and C = -8. |
The following are functions but they are not quadratic functions:
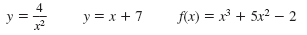
Note:
Notice that in a quadratic function the
variable is in the numerator and the
coefficient of the x2 term is not zero.
Note that y = 4x2 + 5 can be written as
y = 4x2 + 0x + 5.
You may need to simplify a function to
determine if it is quadratic. For example:
| f(x) |
= x3 + x(5x - x2) + 6
= x3 + 5x2 - x3 + 6
= 5x2 + 6 |
This is a quadratic function because it can
be written in the form f(x) = Ax2 + Bx + C where A = 5, B = 0, and C
= 6.
|