Inequalities
The aim of this document is to provide a short, self-assessment
programme for students who wish to acquire a basic competence in
the use of inequalities.
A number a is greater than a number b if a - b is positive. In
symbols this is written as a > b.
Thus
2 > 1 because 2 - 1 = 1 is positive,
3 > - 1 because 3 - ( - 1) = 4 is positive,
BUT
- 1 > 2 is false because - 1 - 2 = - 3 is negative.
Example 1
Prove or disprove the following inequalities.

Solution
(a) As a decimal, 1/4 = 0.25 and so 0.4 - 1/4
= 0.4 - 0.25 = 0.15, which is positive. Thus 0.4 > 1/4 is
true.
(b) Here (0.7)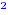 = 0.7 ×
0.7 = 0.49. As a fraction 1/2 is 0.5. In this case, (0.7) = 0.7 ×
0.7 = 0.49. As a fraction 1/2 is 0.5. In this case, (0.7)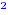 - 1/2 =
0.49 - 0.5 = - 0.01, which is negative. This means that the
inequality (0.7) - 1/2 =
0.49 - 0.5 = - 0.01, which is negative. This means that the
inequality (0.7)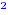 > 1/2 is false. > 1/2 is false.
For this latter example we would write (0.7)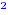 < 1/2,
or in words, (0.7) < 1/2,
or in words, (0.7)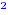 is less than 1/2. is less than 1/2.
In general we say:
A number a is less than a number b if a - b is negative. In
symbols this is written as a < b.
If a < b the b > a and vice versa.
Example 2
In each of the following pairs of numbers, use one of the
symbols > or < to give the correct ordering of the numbers
for the order in which they appear.

Solution
(a) Taking a = - 1 and b = 2 the difference a
- b , becomes a - b = (-1) - 2 = - 3 , which is negative. The
correct inequality is - 1 < 2.
(b) In decimal form 1/4 = 0.25 and 1/5 = 0.2.
Since 0.25 - 0.2 = 0.05, and this is positive, the correct
inequality is 1/4 > 1/5.
In addition to these two inequalities there are two further
symbols, 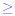 and and 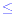 . The first of these is read as greater
than or equal to and the second as less than or
equal to. . The first of these is read as greater
than or equal to and the second as less than or
equal to.
Exercise
For each of the following pairs of numbers use one of the
symbols >, <, 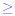 , , 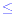 to give the correct ordering for the
order in which they appear. to give the correct ordering for the
order in which they appear.

Solutions
(a) 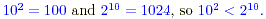
(b) (-1)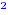 = 1 and
(-1/2) = 1 and
(-1/2)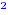 = 1/4 so (-1) = 1/4 so (-1)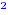 > (-1/2) > (-1/2)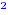 . .
(c) In decimal form 1/ 5 = 0.2 so 0.2 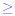 1/ 5
and 0.2 1/ 5
and 0.2 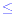 1/ 5 are both true. 1/ 5 are both true.
(d) The solution to this can be obtained by
converting the fractions to decimals as in previous cases. It may
also be obtained using fractions, by writing both with the same
denominator 6.
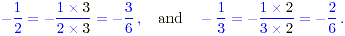
Then
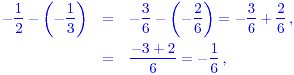
which is negative. The correct inequality is therefore
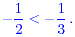
Quiz
Determine which of the following inequalities is correct.
(a) 3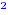 > 2 > 2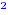 , (b) 2 , (b) 2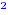 < 4 < 4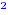 , (c) 2 , (c) 2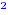 < 5 < 5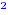 , (d) 3 , (d) 3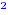 > 4 > 4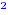
Solution
The solution to this is obtained from 3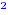 = 9 and
2 = 9 and
2 = 8 and 9 > 8.
= 8 and 9 > 8.
|